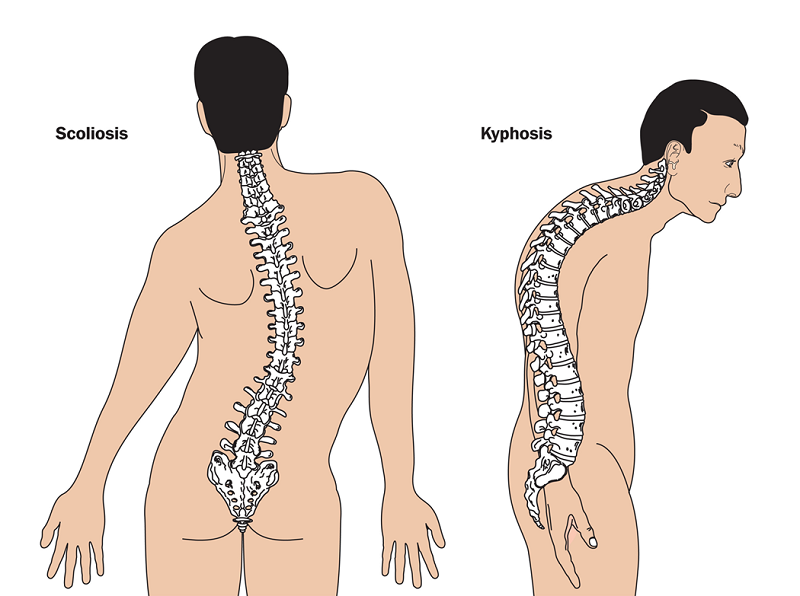
Scoliosis is a condition where a person’s spine is curved to one side. The curvature may look slight or unnoticed, but in some cases, the curvature is enough to make the sufferer disfigured.
Causes
There are many known types of scoliosis, including the following:
Congenital – In the case of a congenital scoliosis sufferer, the curvature is present at birth, and may be caused by an abnormality that can be present even in the womb.
Neuromuscular – This kind of scoliosis is usually seen as a symptom or end-result of people who have abnormal muscle or nerve disorders, such as spina bifida or cerebral palsy. It may also because of medical disorders that can paralyze the sufferers’ body.
Degenerative – Degenerative scoliosis happens when a person has had a major injury or sickness that has caused bone collapse in the spine. I can also be the result of major surgery, or osteoporosis.
Idiopathic scoliosis – While this is the most common form of scoliosis, no one really knows why it happens. One of the few leads so far is that it could be inherited.
What are the numbers?
Around 3% of people aged 16 and below have scoliosis, and considerably fewer than that have spinal curvatures that are greater than 40 degrees, at which point surgery becomes a serious option. Traditionally, girls are more likely to be scoliosis sufferers than boys, particularly in cases for idiopathic scoliosis. Luckily, idiopathic scoliosis seems to stop once patients reach adulthood.
How is it diagnosed?
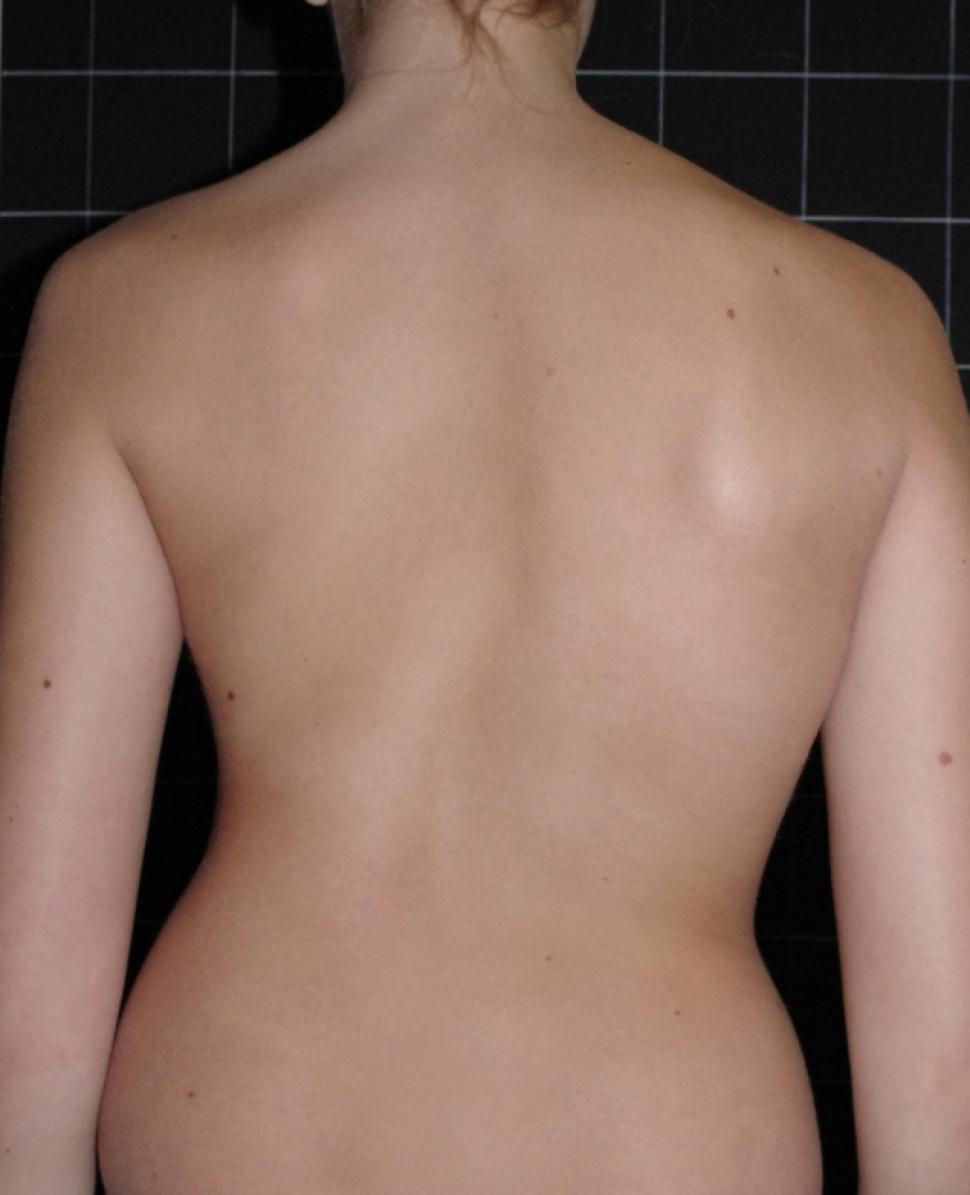
Given the age bracket at which scoliosis happens, most cases are usually detected during exams by pediatricians, or during school physical exams. Physical clues include uneven shoulders, one prominent shoulder blade, a leaning stance to one side, or an uneven waist. Once the initial diagnosis is carried out, a series of X-rays and a bone exam will be used to find out how severe the situation is.
How is scoliosis treated?
Most children and teenagers with idiopathic scoliosis are observed every six months, so that their scoliosis can be monitored. However, in some cases, more active treatment is needed.
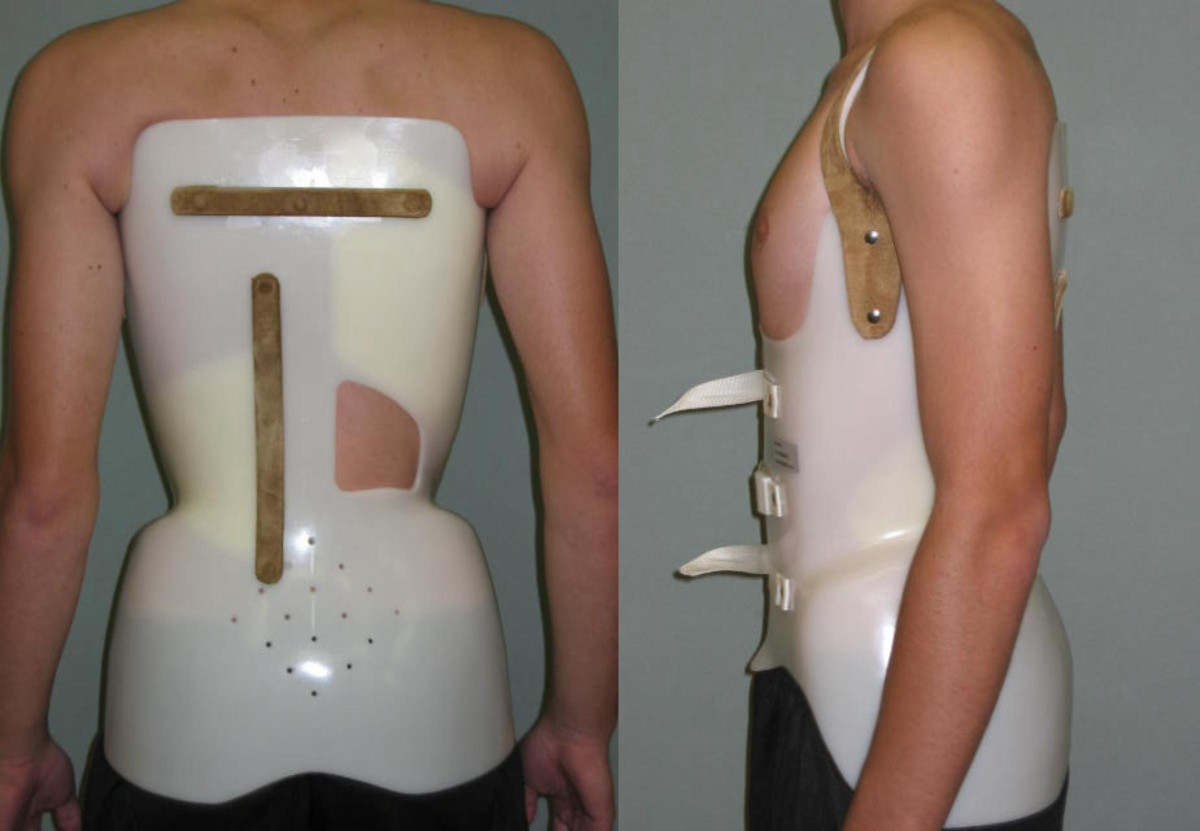
Back braces – if the patient has between 25 and 40 degrees of spinal curvature, braces will usually be used, particularly if they have a minimum of two years remaining in their calculated growth spurt period. Bracing doesn’t improve the curvature, but it will prevent the curve from progressing.
Surgery – If the curvature goes beyond 50 degrees, then surgery becomes a major consideration. The procedure installs metallic implants that act as braces to correct the curve as best as can be done, while the second part of the operation involves the use of bone grafts to permanently fuse sections of the spine together. This option is usually done after the growth spurt, as fusing the bones in the spinal column will stop their growth.
There is another technique that can be used for younger patients, which does not involve spinal fusion. However, a back brace must be always be worn after surgery.
For all patients, an active lifestyle, proper exercise, and a good diet are always encouraged.